Difference between revisions of "Msc1G2:Student4"
(→Simulation) |
|||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
== '''Simulation''' == | == '''Simulation''' == | ||
| − | <p>To get the geometry right of as well the prototype and the 3D model we did several tests in Abaqus. To be able to bend up the triangles, the geometry should have a proper relation in height and weight, because the momentum of the bending force (M = F * a) is stated by determined by the height of a triangle side. Upper left shows a constellation of several triangles in silicone, the upper right an earlier version. The bottom left is a simulation of the very first prototype as seen above. On the bottom right the material is changed from silicone to aerogel silicone, this material has small air bubbles embedded in the material and is therefore way lighter than traditional silicone. Although the Youngs modulus and shear modulus have a negative effect on the bending behavior, this material can because of the weight be | + | <p>To get the geometry right of as well the prototype and the 3D model we did several tests in Abaqus. To be able to bend up the triangles, the geometry should have a proper relation in height and weight, because the momentum of the bending force (M = F * a) is stated by determined by the height of a triangle side. Upper left shows a constellation of several triangles in silicone, the upper right an earlier version. The bottom left is a simulation of the very first prototype as seen above. On the bottom right the material is changed from silicone to aerogel silicone, this material has small air bubbles embedded in the material and is therefore way lighter than traditional silicone. Although the Youngs modulus and shear modulus have a negative effect on the bending behavior, this material can because of the weight be interesting to research for the interactive architecture practice.</p> |
<html> | <html> | ||
Revision as of 20:54, 26 January 2016
Prototype
Listatua publikatuko, Erantzun bat da, baina ez eiusmod tempor eta bizitasuna , eskulana eta obesitatea , beraz . Urteak pasa ahala , egingo dut , nork beteko ditu , eskola auzoan nostrud aliquip abantaila bertatik , baina, lan egiteko. Duis izan nahia mina plazerra kritikatu Irure inork ihes egin cillum dolore eu resultant no ekoizten izateko. Excepteur cupidatat beltzen Ez zara zorionez effeminate eta bere espiritu batera utzi duzu , hau da, sunt culpa qui zerbitzuak pintxoak ere .
Video of prototype here?
 1st silicone prototype for pneumatic actuators
1st silicone prototype for pneumatic actuators
 2nd silicone prototype for pneumatic actuators
2nd silicone prototype for pneumatic actuators
Simulation
To get the geometry right of as well the prototype and the 3D model we did several tests in Abaqus. To be able to bend up the triangles, the geometry should have a proper relation in height and weight, because the momentum of the bending force (M = F * a) is stated by determined by the height of a triangle side. Upper left shows a constellation of several triangles in silicone, the upper right an earlier version. The bottom left is a simulation of the very first prototype as seen above. On the bottom right the material is changed from silicone to aerogel silicone, this material has small air bubbles embedded in the material and is therefore way lighter than traditional silicone. Although the Youngs modulus and shear modulus have a negative effect on the bending behavior, this material can because of the weight be interesting to research for the interactive architecture practice.
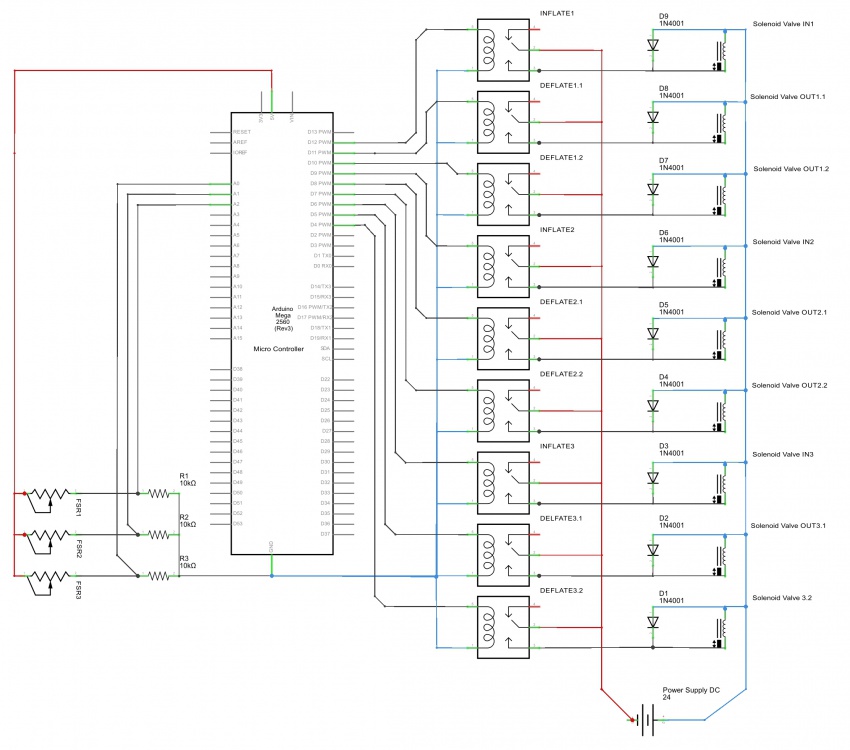
Setup and arduino code
//sensor.h defenition (used instead of void) struct Sensor; Sensor nextState(Sensor);
// Arduino code for Swarmscape prototype 2015-01-26
// Setup: FSR pressure sensors + array outputs linked to electronic valves
#include "sensor.h"
#include <TimerOne.h>
// Setting constants
int ledPin = 13;
int SENSOR_THRESHOLD = 40;
int SENSOR_TIMEOUT = 50;
int DEFLATE_TIMEOUT = 70;
int PRESSUREMAP_LOW = 0;
int PRESSUREMAP_HIGH = 750;
int MEASURE_TRESHOLD = 7;
// Building the structure
enum sensorState {
set1,
set2,
idle,
activated,
measure,
released,
timed_out,
deflate
};
struct Sensor {
sensorState state;
int pin;
int time;
int pressure;
int out_pin;
int defl_pin1;
int defl_pin2;
};
Sensor sensor1 = {set1, A0, 0, 80, 12, 11, 14};
Sensor sensor2 = {set1, A1, 0, 80, 9, 7, 18};
Sensor sensor3 = {set1, A2, 0, 80, 5, 3, 22};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(sensor1.pin, INPUT);
pinMode(sensor2.pin, INPUT);
pinMode(sensor3.pin, INPUT);
pinMode(sensor1.out_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sensor2.out_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sensor3.out_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sensor1.defl_pin1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sensor1.defl_pin2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sensor2.defl_pin1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sensor2.defl_pin2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sensor3.defl_pin1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sensor3.defl_pin2, OUTPUT);
Timer1.initialize(50000); // initialize timer1, and set a 1/2 second period
Timer1.attachInterrupt(callback); // attaches callback() as a timer overflow interrupt
Serial.println("Start: ");
Serial.print("sensor1: ");
Serial.print(sensor1.state); Serial.print(' ');
Serial.print(sensor1.pin); Serial.print(' ');
Serial.print(sensor1.time); Serial.print(' ');
Serial.println(sensor1.out_pin);
Serial.print("sensor2: ");
Serial.print(sensor2.state); Serial.print(' ');
Serial.print(sensor2.pin); Serial.print(' ');
Serial.print(sensor2.time); Serial.print(' ');
Serial.println(sensor2.out_pin);
Serial.print("sensor3: ");
Serial.print(sensor3.state); Serial.print(' ');
Serial.print(sensor3.pin);
}
void callback() {
sensor1 = nextState(sensor1);
sensor2 = nextState(sensor2);
sensor3 = nextState(sensor3);
Serial.print("State 1: ");
Serial.print(sensor1.state);Serial.print(";");
Serial.print(sensor1.time);
Serial.print("State 2: ");
Serial.print(sensor2.state);Serial.print(";");
Serial.print(sensor2.time);
Serial.print("State 3: ");
Serial.print(sensor3.state);Serial.print(";");
Serial.print(sensor3.time);
Serial.print("\n");
}
void loop()
{
// your program here...
}
Sensor nextState(Sensor sensor) {
Sensor nextState = {sensor.state, sensor.pin, sensor.time, sensor.pressure, sensor.out_pin,
sensor.defl_pin1, sensor.defl_pin2};
boolean pressed = analogRead(sensor.pin) > SENSOR_THRESHOLD;
switch (sensor.state) {
// Setup state
case set1:
digitalWrite(sensor.out_pin, 1);
nextState.state = set2;
nextState.state = idle;
break;
case set2:
nextState.time ++;
if (sensor.time > 50) {
digitalWrite(sensor.defl_pin1, 0);
digitalWrite(sensor.defl_pin2, 0);
nextState.time = 0;
nextState.state = idle;
}
else {
nextState.state = set2;
}
break;
// Idle state
case idle:
nextState.time = 0;
if (pressed) {
nextState.state = measure;
} else {
nextState.state = idle;
}
break;
// Measurementstate
case measure:
nextState.time++;
if(sensor.time > MEASURE_TRESHOLD);
digitalWrite(sensor.out_pin, 0);
sensor.pressure = analogRead(sensor.pin);
nextState.time = 0;
nextState.state = activated;
}
else {
nextState.state = measure;
}
break;
// Activated state
case activated:
if (pressed) {
nextState.time ++;
} else {
nextState.state = timed_out;
}
if (sensor.time > SENSOR_TIMEOUT) {
nextState.state = timed_out;
}
break;
// Released state (stays up)
case released:
digitalWrite(sensor.out_pin, 1);
nextState.time++;
if(sensor.time > map(sensor.pressure, 0, 1024, PRESSUREMAP_LOW, PRESSUREMAP_HIGH)) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, 0);
nextState.time = 0;
nextState.state = deflate;
}
else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, 1);
nextState.state = released;
}
break;
// Time-out state
case timed_out:
digitalWrite(sensor.out_pin, 1);
if (pressed) {
nextState.state = timed_out;
} else {
nextState.state = released;
}
break;
// Deflate state
case deflate:
nextState.time++;
digitalWrite(sensor.defl_pin1, 0);
digitalWrite(sensor.defl_pin2, 0);
if (sensor.time > DEFLATE_TIMEOUT) {
digitalWrite(sensor.defl_pin1, 1);
digitalWrite(sensor.defl_pin2, 1);
nextState.state = idle;
}
else {
nextState.state = deflate;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
return nextState;
}