Difference between revisions of "Shared:Group 1"
Marco Galli (Talk | contribs) (→METROPOLITAN) |
Marco Galli (Talk | contribs) (→METROPOLITAN) |
||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
[[File:Rtdm2-08.jpg|850px]] | [[File:Rtdm2-08.jpg|850px]] | ||
[[File:SITE1-08.png|850px]] | [[File:SITE1-08.png|850px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 01:24, 21 September 2015
Milou van Min | Lars van Vianen | Marco Galli
Contents
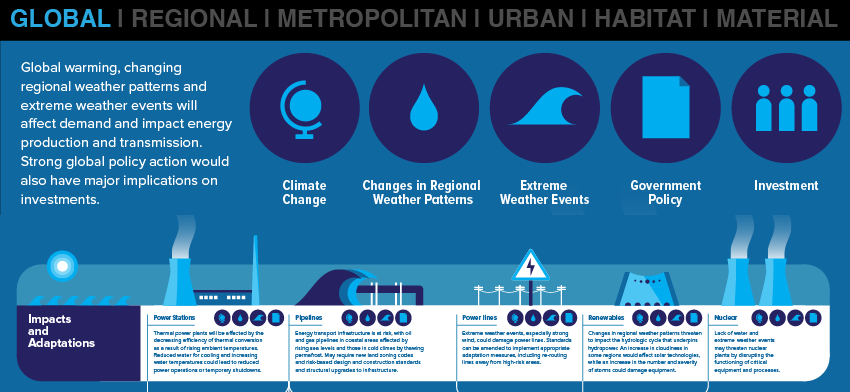
GLOBAL | Climate Change
Energy Sector Faces Major Challenges from Climate Change Without strong mitigation policies, the global average temperature is likely to rise above the internationally agreed 2°C target. As a major source of carbon emissions, the energy sector will be aected by mitigation policies as well as by climate impacts in multiple ways.
check out complete infographic: http://www.desmog.ca/sites/beta.desmogblog.com/files/IPCC_AR5__Implications_for_Energy__Infographic__WEB_EN.pdf
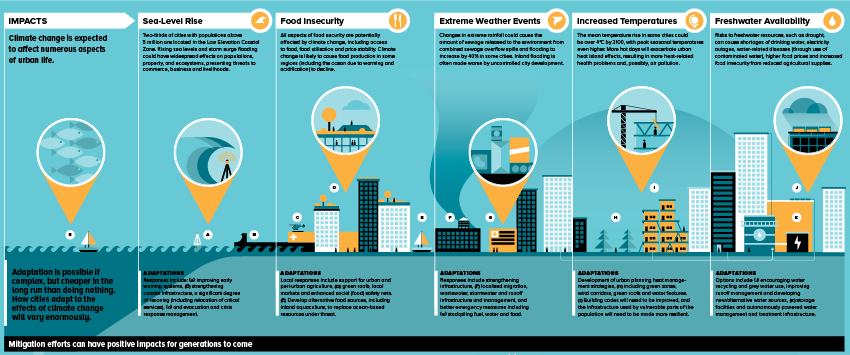
Cities on the front line of a changing climate Urban centres account for more than half of the world’s population, most of its economic activity and the majority of energy-related emissions. The role of cities in reducing emissions and protecting their inhabitants is therefore central to effective climate policies.
check out complete infographic: http://www.desmog.ca/sites/beta.desmogblog.com/files/IPCC_AR5__Implications_for_Cities__Infographic__WEB_EN_0.pdff
Infographics extracted from: http://www.desmog.ca/2014/09/05/what-does-climate-adaptation-actually-look-check-out-awesome-new-infographic-series-cambridge
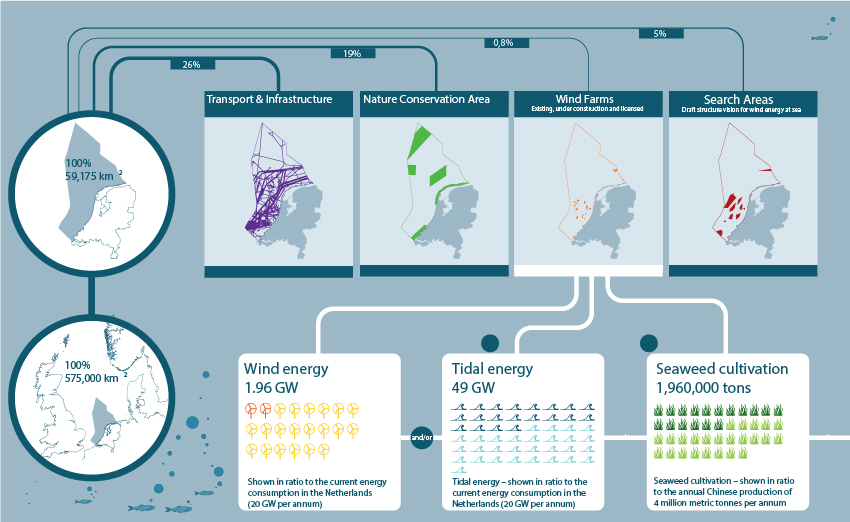
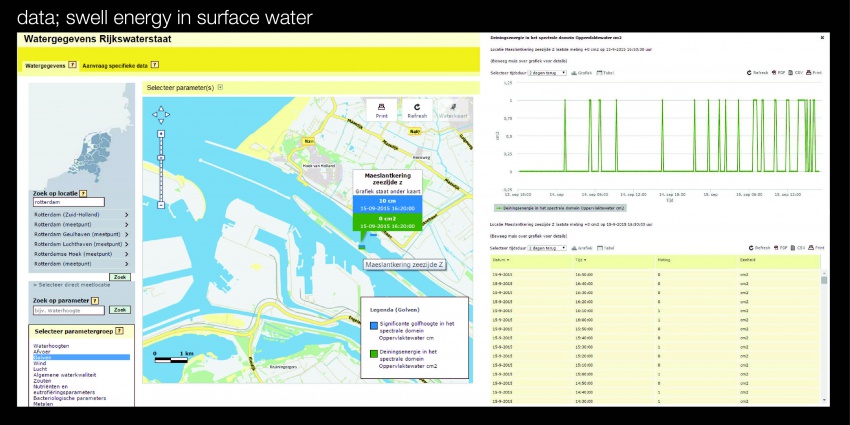
REGIONAL | The North Sea
North Sea 2050 Spatial Agenda
From the vision on the North Sea in 2050, the spatial agenda mentions five themes on which I would like to focus:
1) building with North Sea nature;
2) energy transition at sea; challenge is to be economical with space and utilise opportunities to increase energy generation per square nautical mile. The market for tidal and wave energy is focussing increasingly on being able to convert lower current speeds and limited wave heights found in Dutch waters into electricity.
3) multiple/multi-functional use of the space;
4) connection between land and sea;
5) accessibility/shipping.
A day on the North Sea - 2050 from Must Stedebouw on Vimeo.
Opportunities for sustainable economic development of sea and coast
Extracted from: http://www.noordzeeloket.nl/en/Images/North%20Sea%202050%20Spatial%20Agenda_LO%20RES_3562.pdf
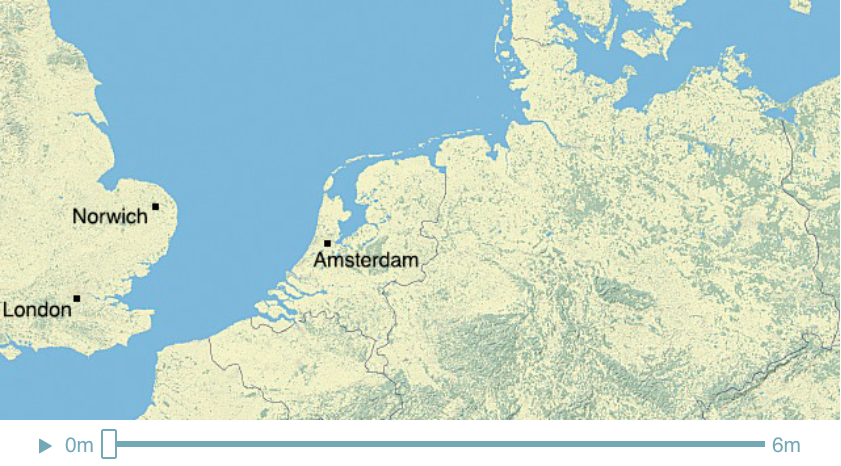
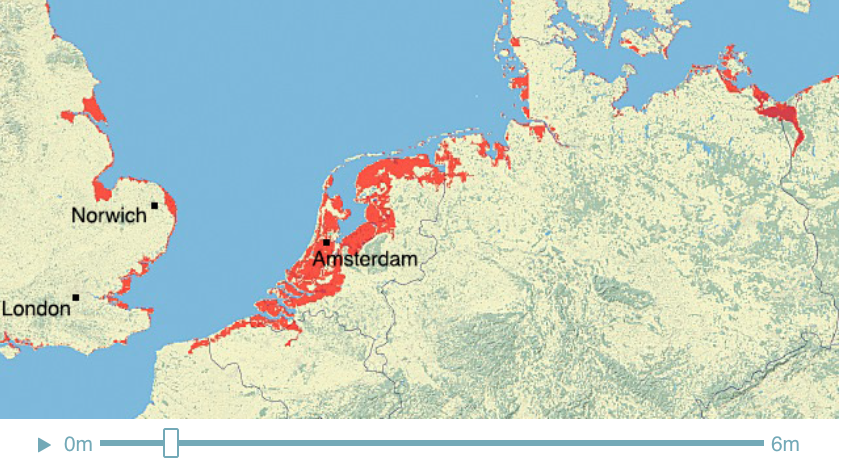
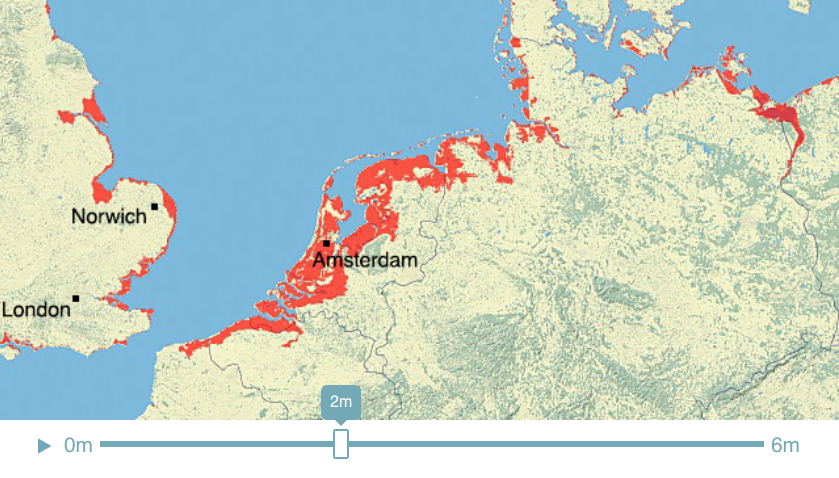
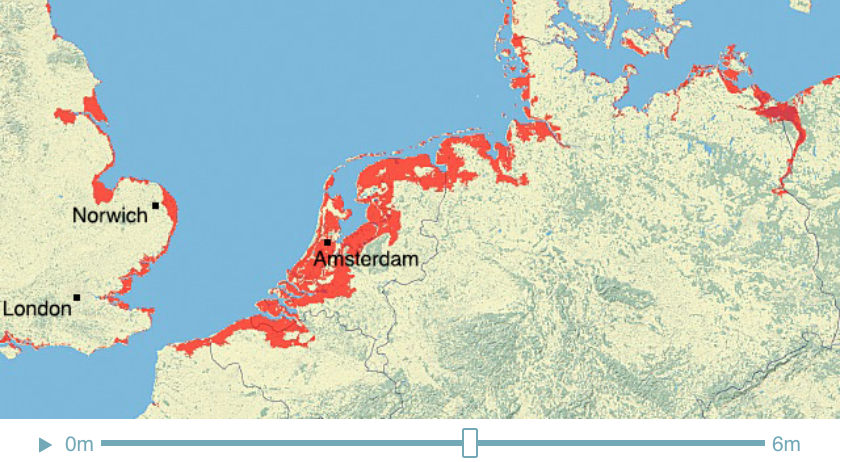
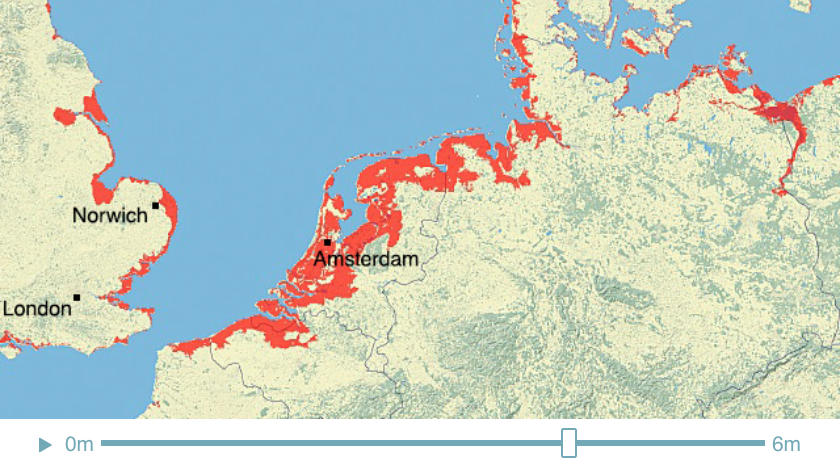
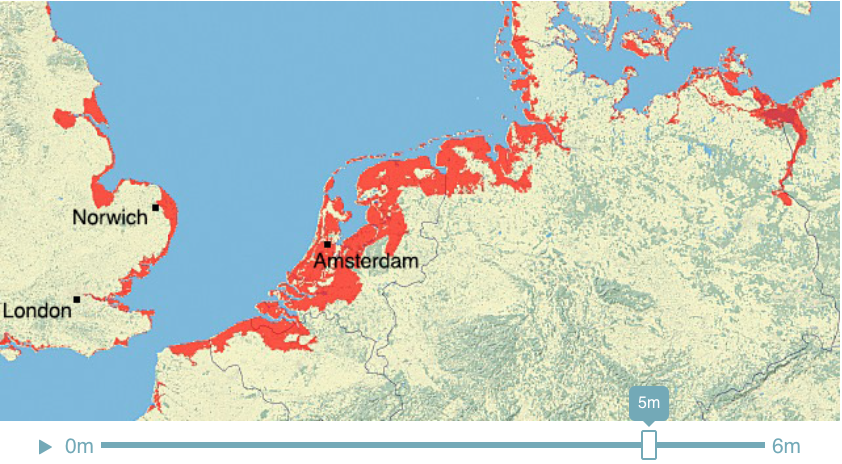
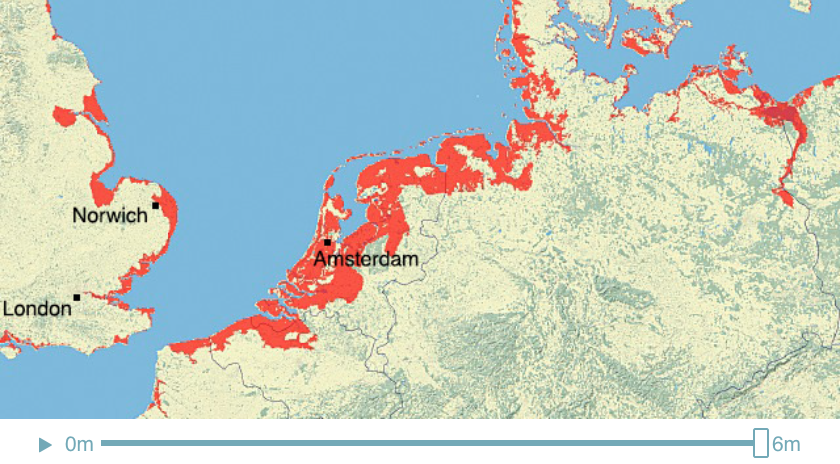
Climate Time Machine Sea Levels - North Sea
Recent satellite observations have detected a thinning of parts of the Greenland ice sheet at lower elevations. A partial melting of this ice sheet would cause a 1-meter (3-foot) rise. If melted completely, the Greenland ice sheet contains enough water to raise sea level by 5-7 meters (16-23 feet).
This visualization shows the effect on coastal regions for each meter of sea level rise, up to 6 meters (19.7 feet). Land that would be covered in water is shaded red.
Credit: Center for Remote Sensing of Ice Sheets - http://climate.nasa.gov/interactives/climate-time-machine
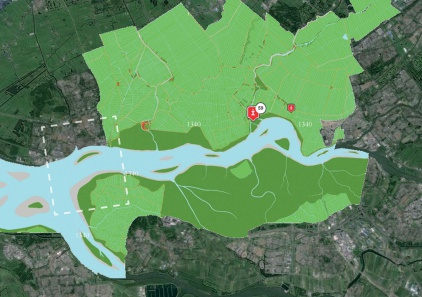
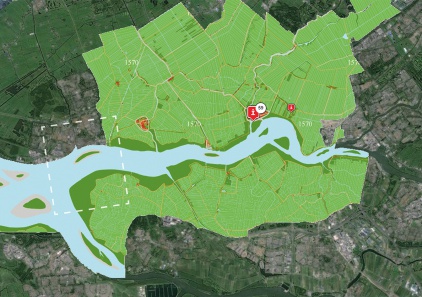
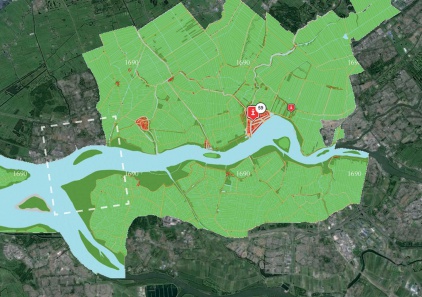
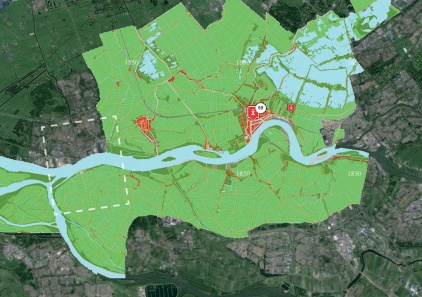
METROPOLITAN
URBAN
LOCAL
MATERIAL
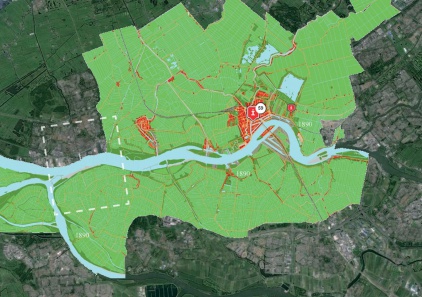
PAST
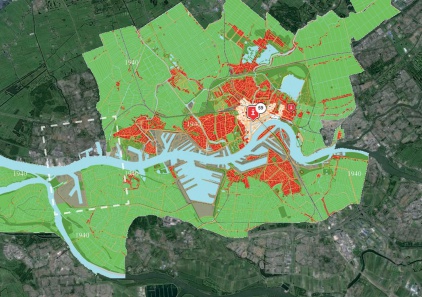
PRESENT
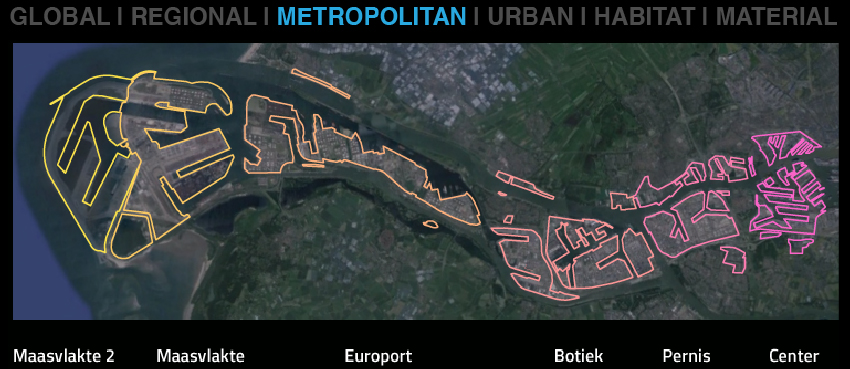
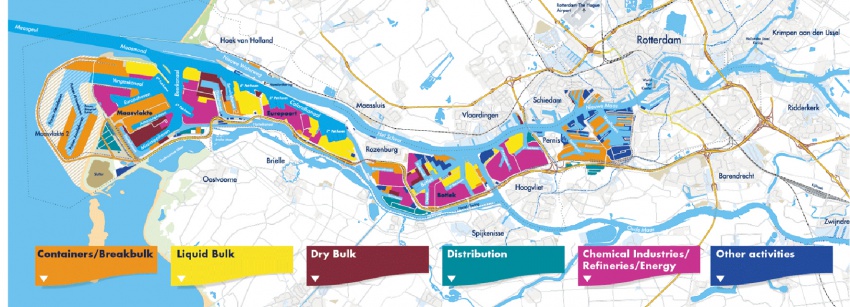
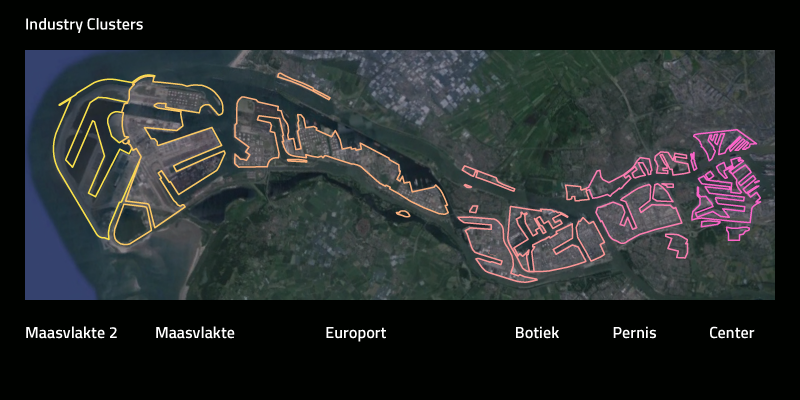
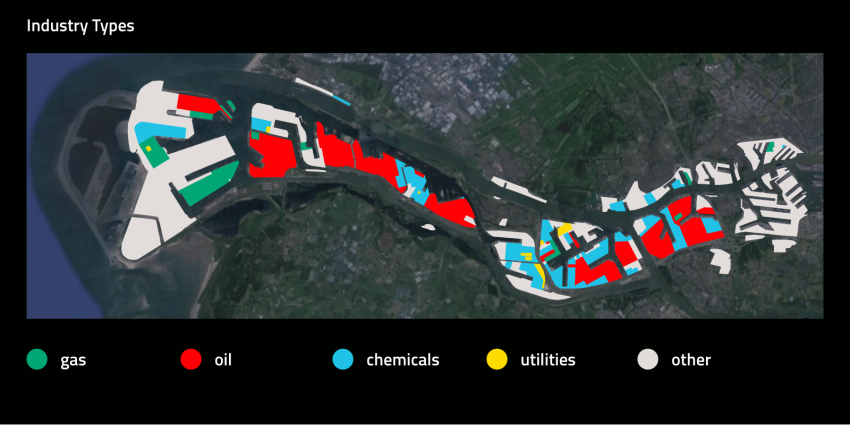
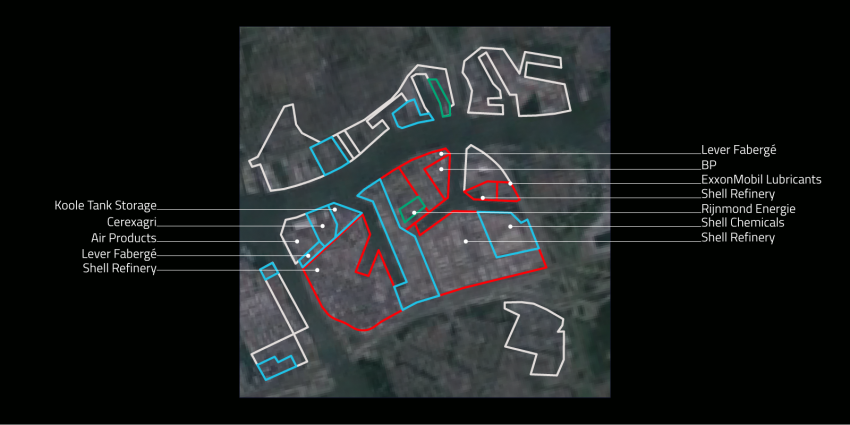
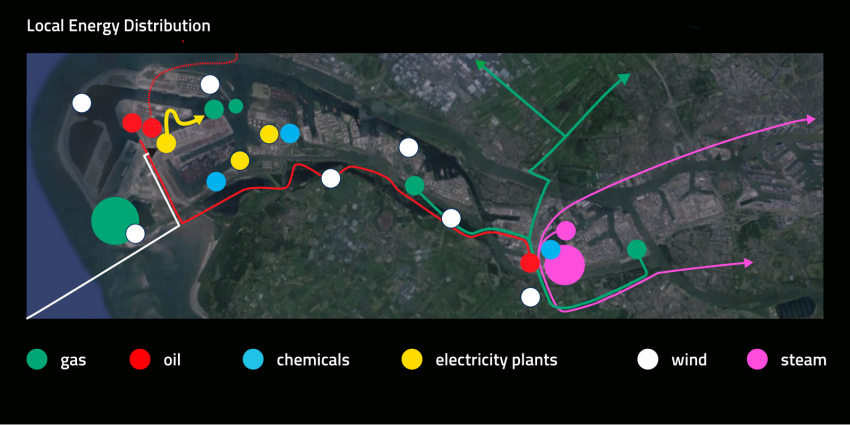
The port of Rotterdam is the engine of the Dutch economy
> total port area of 10,500 ha = 16 000 football fields
> 90 000 people work in the port
> 300,000 people work in total and for the port
> handling 430 million tons, 11 million containers
> the largest port in Europe; No. 5 in the world
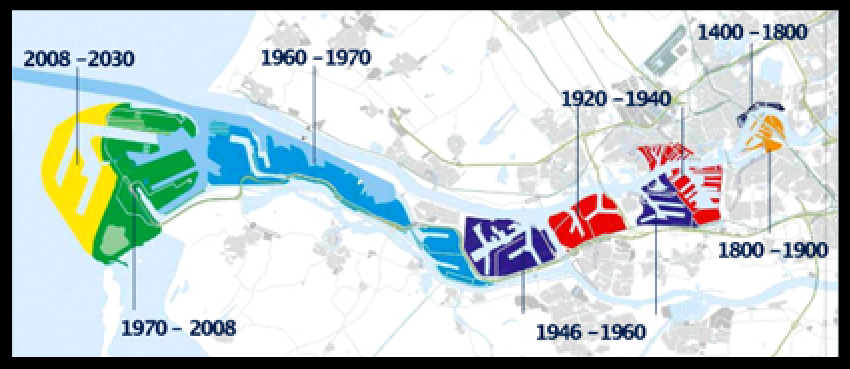
Since the inception of Rotterdam, in the Middle Ages had a port with a transfer function
The High Street, part of Schielands High seafront, divided Rotterdam in a country town and a water city. In the city of waters the first ports were built, including the Old Port, the Haringvliet, Leuvehaven.
During the 19th century, Rotterdam was less accessible. Therefore, the New Waterway was dug so that Rotterdam had a direct connection to the sea.
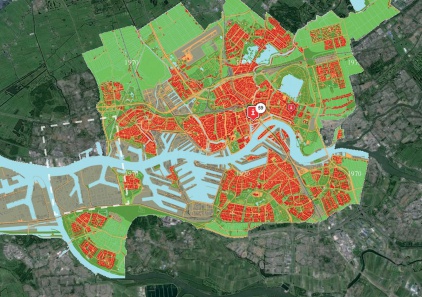
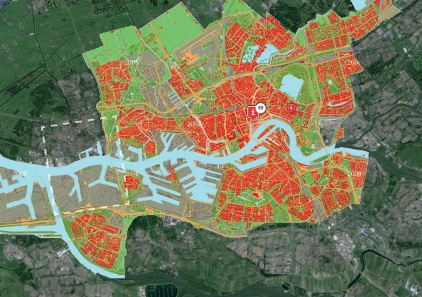
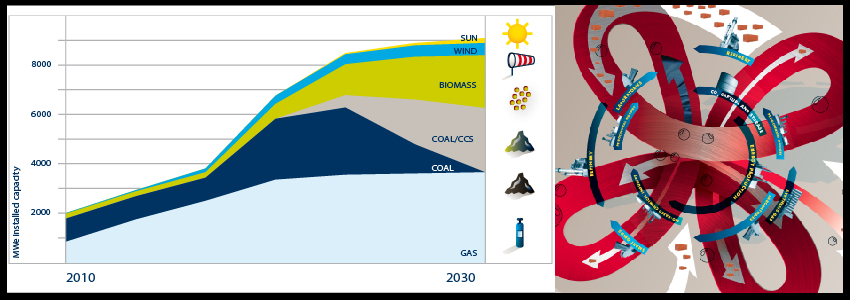
FUTURE
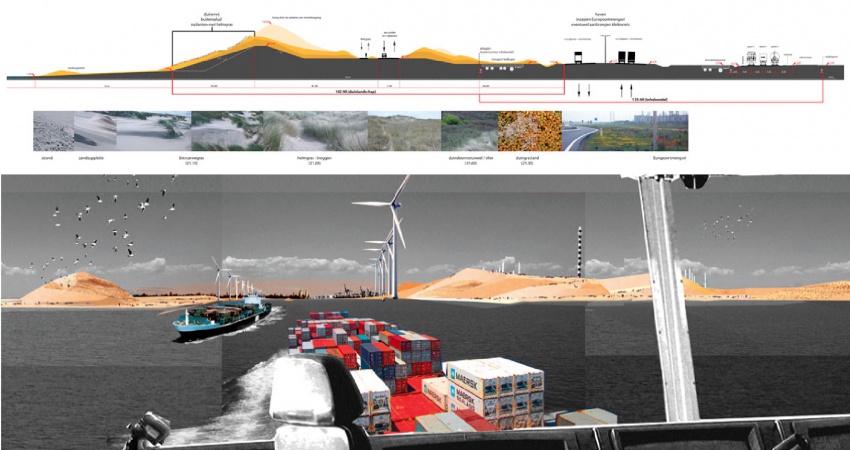
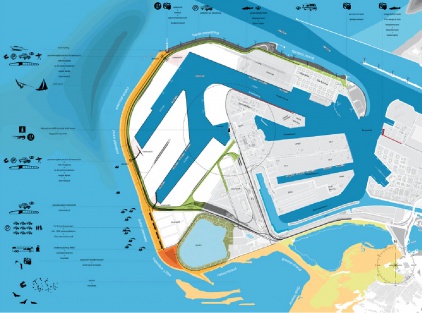
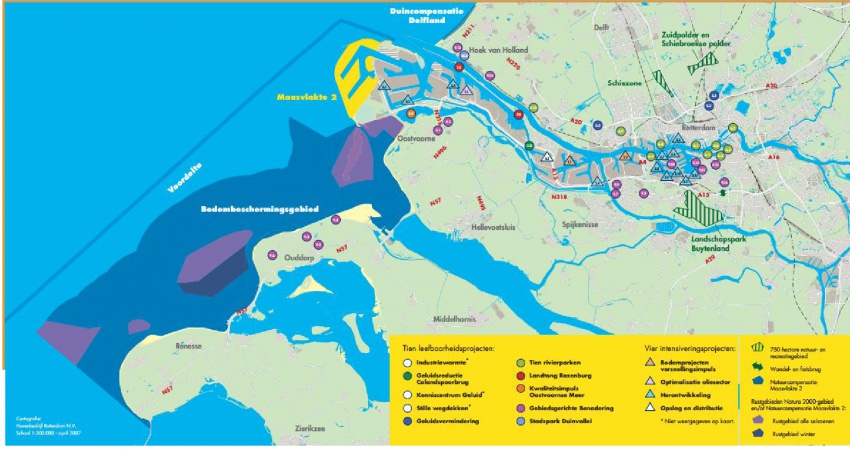
Maasvlakte 2 Landscape Plan
The Port of Rotterdam has planned a westward extension of its harbor area to provide for future growth. The land reclamation project called Tweede Maasvlakte (MV2 or “Second Maas Mudflats” - there is already a first Maasvlakte) is intended to provide space for industrial activities such as container transhipment, chemicals and distribution. The total area involved is about 2,000 hectares, of which 1,000 hectares nett is issuable for harbor, industrial and commercial activities.
Besides being an extension of the Port of Rotterdam, the MV2 plan has a coastal extension component. New sand dunes and dykes will be required to assure the safety of the land reclaimed form the North Sea. The target for the start of land reclamation and the sand excavation which will make it possible is in 2008.
The Port of Rotterdam intends to combine the creation of land for new harbor activities on MV2 with space for recreation and new nature areas. H+N+S was invited to prepare a plan for this “harbor landscape” in 2007. There are three aspect of the harbor which affect the design and landscaping of MV2. Firstly, there is the technical reality of the harbor industry; secondly, a harbor for nature; and thirdly, an accessible, attractive harbor for the public. In the master landscape plan for MV2, H+N+S has combined these three “realms” or “themes” into an appealing concept, and has also worked out detailed landscaping designs. The outcome is a sturdy, large-scaled landscape with long lines of sight, robust viaducts, a large beach for high-capacity leisure use and a “super lookout dune”. There is also room for a bird valley, moist dune valleys and bird-spotting sites.
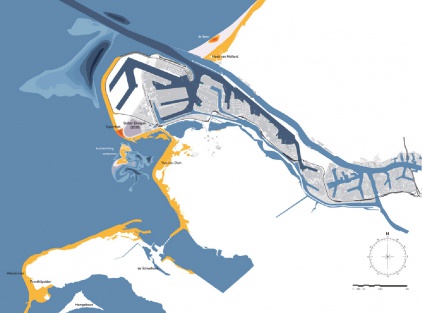
The Happy Isles Consortium
The Happy Isles Consortium - West 8 and Svasek– drew up a plan which combines an agenda for safety, and the necessity of new land. The participants offer the metropolis a new perspective by proposing a series of new, sprayed-up sand islands off the coast of Belgium and The Netherlands. These dune islands, measuring up to 150.000 hectares in size, will break the increasing waves. Also, thanks to ingenious engineering of the gullies, the off-shore under tow will cause the sea level to drop during north-western storms.
On the biggest island, Hollandsoog, 150.000-200.000 ha. in size, a broad representation of the community will be able to obtain a lease. The economy of this island will be based on leisure and nature experience; a happy island for family, lonely-hearts, poets and festivals.
http://www.west8.nl/projects/all/happy_isles/
WORLD EXPO ROTTERDAM 2025